
1. Presence of p waves
2. Width of QRS complexes
3. Relationship between the p waves and QRS complexes
4. Any presence of unusual complexes
5. Life threatening
6. Supraventricular (Abnormal depolarisation generates above the ventricles) or Ventricular (within the ventricles)
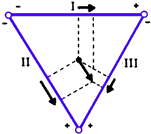
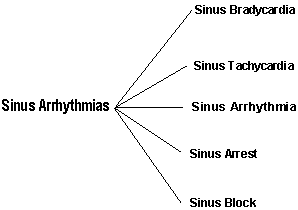
![]() Sinus arrhythmias- Disturbance in impulse discharge or conduction from the pacemaker (SA node).
Sinus arrhythmias- Disturbance in impulse discharge or conduction from the pacemaker (SA node).
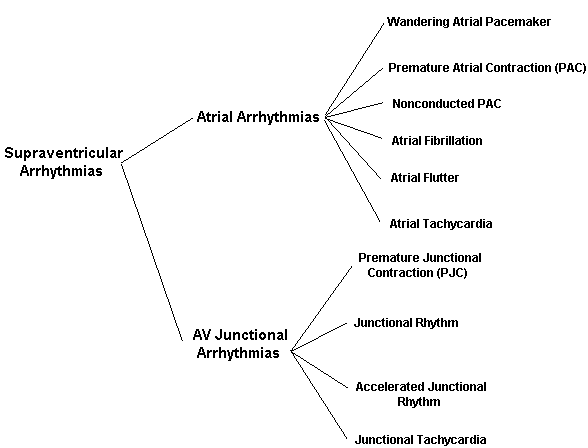
![]() Premature atrial contraction- A single or multiple ectopic pacemaker site(s) in the atria. P waves will be abnormal, QRS and T will have the same configuration as sinus beat.
Premature atrial contraction- A single or multiple ectopic pacemaker site(s) in the atria. P waves will be abnormal, QRS and T will have the same configuration as sinus beat.
![]() Nonconducted PAC- P wave of a nonconducted ectopic atrial focus, premature, abnormal in size and shape or direction.
Nonconducted PAC- P wave of a nonconducted ectopic atrial focus, premature, abnormal in size and shape or direction.
![]() Atrial fibrillation- Several micro re-entrant circuits (at least 6) discharging the atria at a rate of 400/min or more. Variable atrial activites may resembles p waves, totally irregular narrow QRS complexes
Atrial fibrillation- Several micro re-entrant circuits (at least 6) discharging the atria at a rate of 400/min or more. Variable atrial activites may resembles p waves, totally irregular narrow QRS complexes
![]() Atrial flutter- Single re-entrant circuit in the atria discharging the atria at a regular rate of 250-400/min. P waves has a sawtoothed pattern, physiological block occurs at the AV node when atrial rate exceeds 180/min, therefore (p wave : QRS) ratio is usually 2:1, 3:1 or 4:1
Atrial flutter- Single re-entrant circuit in the atria discharging the atria at a regular rate of 250-400/min. P waves has a sawtoothed pattern, physiological block occurs at the AV node when atrial rate exceeds 180/min, therefore (p wave : QRS) ratio is usually 2:1, 3:1 or 4:1
![]() Atrial tachycardia- Ectopic reentry circuit involving the atria and AV node, or an accessory pathway involving the atria and ventricle. P waves will be abnormal, at a rate of 130-250/min, may be hidden in the T wave of the preceding beat.
Atrial tachycardia- Ectopic reentry circuit involving the atria and AV node, or an accessory pathway involving the atria and ventricle. P waves will be abnormal, at a rate of 130-250/min, may be hidden in the T wave of the preceding beat.
![]() Case 3 - Regular PACs 2(under construction)
Case 3 - Regular PACs 2(under construction)
![]() Case 4 - Regular Atrial Ectopics
Case 4 - Regular Atrial Ectopics
![]() Case 5 - Nonconducted Atrial Contractions
Case 5 - Nonconducted Atrial Contractions
![]() Case 12 - Atrial Fibrillation 1
Case 12 - Atrial Fibrillation 1
![]() Case 13 - Atrial Fibrillation 2
Case 13 - Atrial Fibrillation 2
![]() Case 14 - Atrial Fibrillation 3
Case 14 - Atrial Fibrillation 3
![]() Case 15 - Atrial Fibrillation 4
Case 15 - Atrial Fibrillation 4
![]() Case 16 - Atrial Fibrillation 5
Case 16 - Atrial Fibrillation 5
![]() Case 20 - Supraventricular Tachycardia 1
Case 20 - Supraventricular Tachycardia 1
![]() Case 21 - Supraventricular Tachycardia 2
Case 21 - Supraventricular Tachycardia 2
![]() Premature junctional contraction- An ectopic pacemaker in the AV junction. Inverted p wave will occur either before the QRS, after the QRS, or hidden within the QRS complex.
Premature junctional contraction- An ectopic pacemaker in the AV junction. Inverted p wave will occur either before the QRS, after the QRS, or hidden within the QRS complex.
![]() Junctional rhythm- Ectopic pacemaker in the AV junction, with a rate of 40-60/min, regular QRS complex.
Junctional rhythm- Ectopic pacemaker in the AV junction, with a rate of 40-60/min, regular QRS complex.
![]() Accelerated junctional rhythm- Ectopic pacemaker in the AV junction, with a rate exceeds 100/min, regular QRS complex.
Accelerated junctional rhythm- Ectopic pacemaker in the AV junction, with a rate exceeds 100/min, regular QRS complex.
![]() Junctional tachycardia- no p waves, regular narrow QRS complexes.
Junctional tachycardia- no p waves, regular narrow QRS complexes.
![]() Case 1 - Premature Junctional Contraction
Case 1 - Premature Junctional Contraction
![]() Case 3 - Junctional Tachycardia 1
Case 3 - Junctional Tachycardia 1
![]() Case 4 - Junctional Tachycardia 2
Case 4 - Junctional Tachycardia 2
![]() Case 5 - Junctional Tachycardia 3
Case 5 - Junctional Tachycardia 3
![]() Case 1 - Irregular Supraventricular Rhythm 1
Case 1 - Irregular Supraventricular Rhythm 1
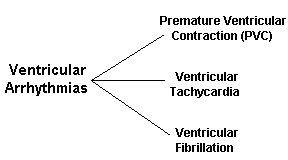
![]() Ventricular Tachycardia- Wide QRS complex, T waves are difficult to see, rate usually regular.
Ventricular Tachycardia- Wide QRS complex, T waves are difficult to see, rate usually regular.
![]() Ventricular Fibrillation- No QRS complex identify, chaotic trace of fibrillation waves
Ventricular Fibrillation- No QRS complex identify, chaotic trace of fibrillation waves
![]() Case 5 - Ventricular Tachycardia 1
Case 5 - Ventricular Tachycardia 1
![]() Case 6 - Ventricular Tachycardia 2
Case 6 - Ventricular Tachycardia 2
![]() Case 7 - Ventricular Tachycardia 3
Case 7 - Ventricular Tachycardia 3
![]() Case 8 - Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
Case 8 - Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia