
Common indications for pacemaker insertion:
Pacemaker Nomenclature:
The following table summarises different type of pacemaker:
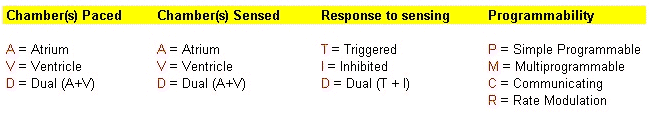
Example: DDD pacemaker - Paces both the atrium and ventricle, senses both atrium and ventricle, is inhibited by atrial output and triggered by a ventricular paced complex after a sensed atrial complex.